CentOS TFTP Server KB ID 0000998
Problem
I needed to back up a Cisco firewall, and perform an upgrade remotely, despite my best efforts to use the ASDM and update via http, I had to go ‘old school’ and bring up a TFTP server on one of my CentOS Linux servers.
Solution CentOS TFTP Server
1. Log onto the server and install the xinetd TFTP Server. Execute the following command and follow the on-screen prompts.
Using username "root".
Last login: Thu Aug 7 17:58:10 2014 from midd-8.cable.virginm.net
[root@Web-Test ~]# yum install tftp tftp-server xinetd2. Now you need to edit the config file, here I’m using nano, but you could use vi as well.
[root@Web-Test ~]# nano /etc/xinetd.d/tftp3. When you open the file it will look like this;
# default: off
# description: The tftp server serves files using the trivial file transfer
# protocol. The tftp protocol is often used to boot diskless
# workstations, download configuration files to network-aware printers,
# and to start the installation process for some operating systems.
service tftp
{
socket_type = dgram
protocol = udp
wait = yes
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.tftpd
server_args = -s /var/lib/tftpboot
disable = yes
per_source = 11
cps = 100 2
flags = IPv4
} 4. Edit the file and save it, so it looks like this;
# default: off
# description: The tftp server serves files using the trivial file transfer
# protocol. The tftp protocol is often used to boot diskless
# workstations, download configuration files to network-aware printers,
# and to start the installation process for some operating systems.
service tftp
{
socket_type = dgram
protocol = udp
wait = yes
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.tftpd
server_args = -c -s /var/lib/tftpboot
disable = no
per_source = 11
cps = 100 2
flags = IPv4
}5. Set the permissions on the tftp folder.
[root@Web-Test ~]# chmod 777 /var/lib/tftpbootNote: if you run SELinux you may also need to execute the following command, ‘setsebool -P tftp_anon_write 1‘.
WARNINIG: This enables anonymous access on the TFTP root folder, if your server is public facing and not firewalled, then I would suggest you do what I do, (stop and start the service manually, and only open the firewall for TFTP when you need to use it – see below).
6. If you use iptables as a firewall, you will need to open the TFTP port (UDP Port 69).
[root@Web-Test ~]# iptables -I INPUT -p udp --dport 69 -j ACCEPT7. Start the xinetd service.
[root@Web-Test ~]# /etc/init.d/xinetd start
Starting xinetd:[ OK ]8. If you want the service to always be running, (see my warning above) then use the following command.
[root@Web-Test ~]# chkconfig xinetd on9. Let’s give it a test, from my Cisco device lets see if I can backup the config to this server.
Petes-ASA# copy run tftp
Source filename [running-config]?
Address or name of remote host []? 123.123.123.123
Destination filename [running-config]? Cryptochecksum: 9d4006ed 0bb1d39c fe61da22 91222a76 !!! 9284 bytes copied in 2.130 secs (4642 bytes/sec) Petes-ASA#
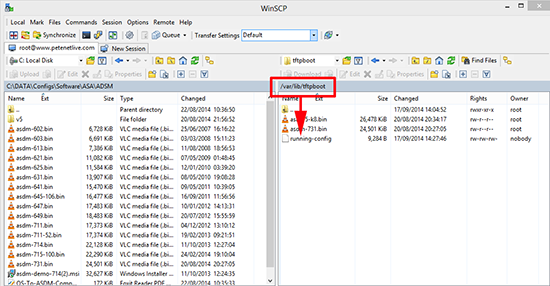
10. I could SSH into the server and change to the /var/lib/tftpboot directory and see the file. But I’ve got WinSCP installed so I can view the backup with that.
11. Let’s see if we can copy a file off the TFTP server back to the firewall.
Petes-ASA# copy tftp flash
Address or name of remote host []? 123.123.123.123
Source filename []? asa915-k8.bin
Destination filename [asa915-k8.bin]?
Accessing tftp://123.123.123.123/asa915k8.bin…!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Writing file disk0:/asa915-k8.bin… !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! 27113472 bytes copied in 845.110 secs (32086 bytes/sec) Petes-ASA#
12. Now unless you are leaving xinetd running lets turn it off.
[root@Web-Test ~]# /etc/init.d/xinetd stop
Stopping xinetd: [ OK ]13. If you are running iptables and have opened the TFTP port I like to close that as well.
Note: It its possible to see that that port is open even if there is no service running on it, that’s why I close it down.
[root@Web-Test ~]# iptables -D INPUT -p udp --dport 69 -j ACCEPTRelated Articles, References, Credits, or External Links
NA
