KB ID 0000944
Problem
This ensures that traffic that is sent over an RDP connection to a server is protected by TLS/SSL Encryption. IT DOES NOT stop clients connecting to an RDP server if they do not have a trusted certificate. If you need that level of security, that should already be done by 802.1x.
Solution
Create an RDP Certificate Template
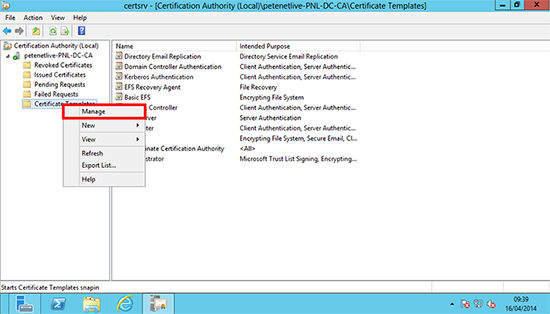
1. On the domain CA Launch the Certification Authority Management Console > Certificates Templates > Right click > Manage.
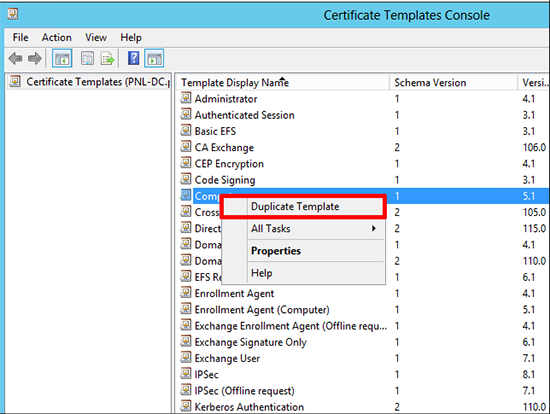
2. Locate, and make a duplicate of, the Computer template.
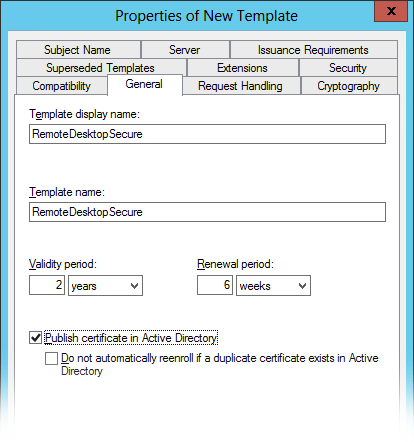
3. General tab > Set the display and template name to RemoteDesktopSecure.
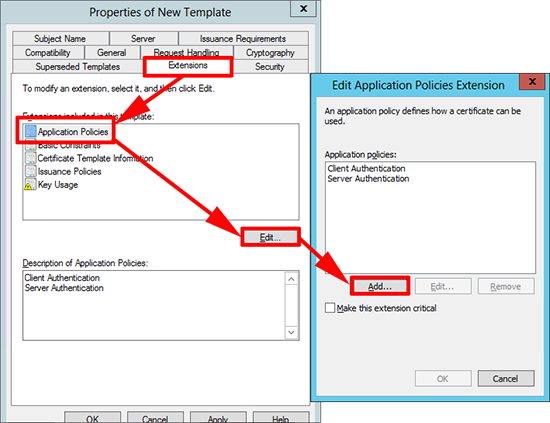
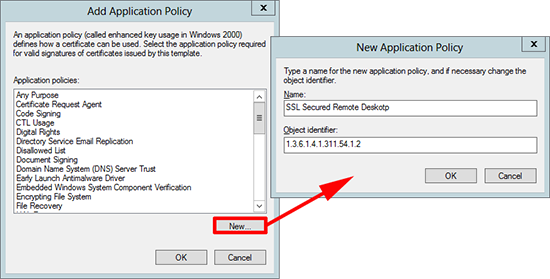
4. Extensions tab > Application Policies > Edit > Add.
5. New > Name=SSL Secured Remote Desktop > Object Identifier=1.3.6.1.4.1.311.54.1.2 > OK.
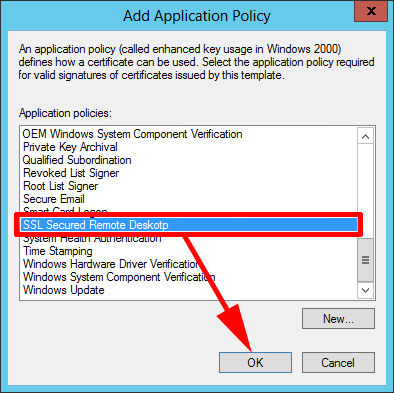
6. Select the policy you have just created > OK.
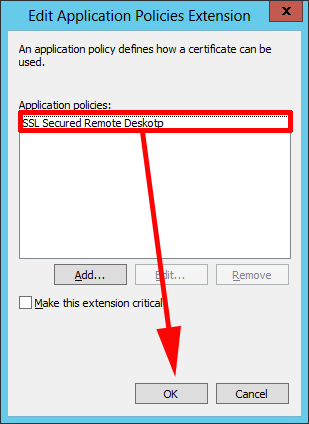
7. Remove the other policies, so only the one we have just created remains > OK.
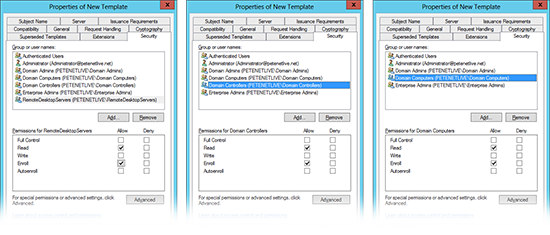
8. Security tab > Ensure that the the computer groups you want to apply the template to, are selected for Read and Enroll. (Below I’ve put three examples, firstly I create a group for my servers, secondly I just apply it to my domain controllers, or lastly I allow all Domain Computers). How you want to apply this depends on you.
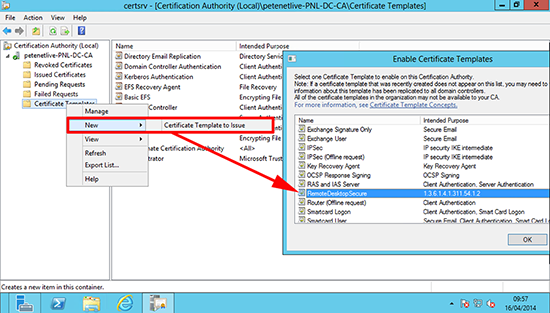
9. Issue/Publish the new certificate template.
Create a GPO to secure RDP access with Certificates.
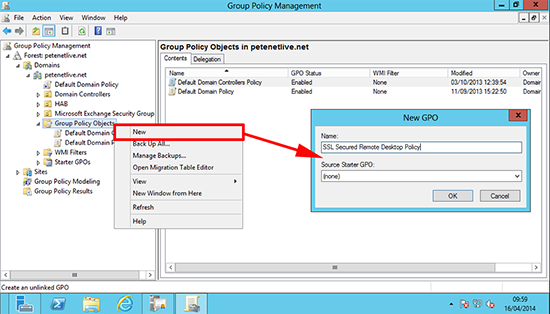
10. From the Group Policy Management Console, create (or edit) a GPO and give it a sensible name.
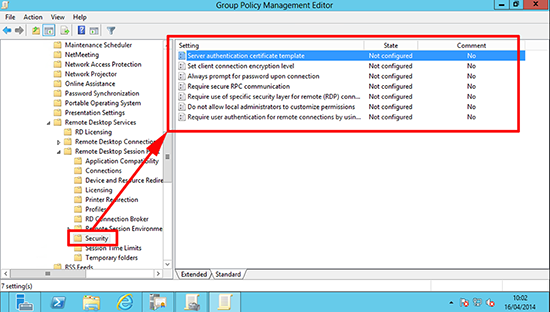
11. Edit that policy and navigate to;
Computer Configuration> Policies >Administrative Templates > Windows > Components > Remote Desktop Services >Remote Desktop Session Host > Security.
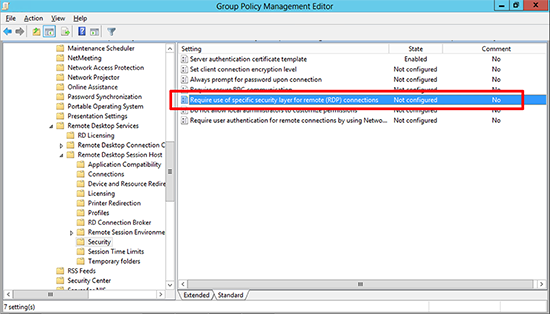
Locate the ‘Server authentication certificate template’ policy.
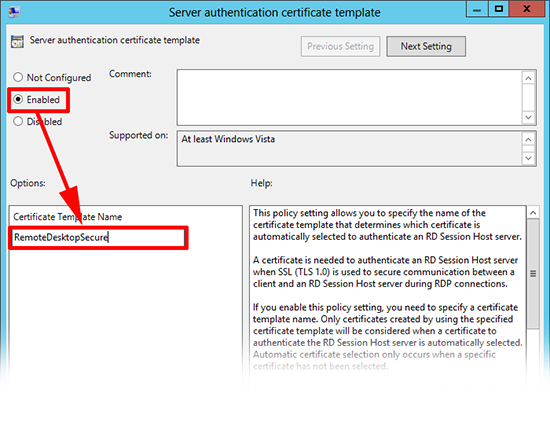
12. Enable it and set the template name to RemoteDesktopSecure > Apply > OK.
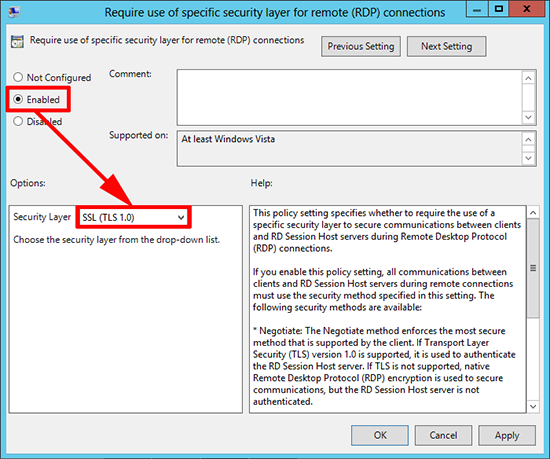
13. In the same location, locate the ‘Require use of specific security layer for remote (RDP) connections’ policy.
14. Enable the policy and set the security layer to SSL (TLS 1.0) > Apply > OK > Exit the policy editor.
15. Link the GPO to an OU that contains the servers you want to apply the policy to.
16. You may need to wait a short while, but eventually the servers will get their certificates.
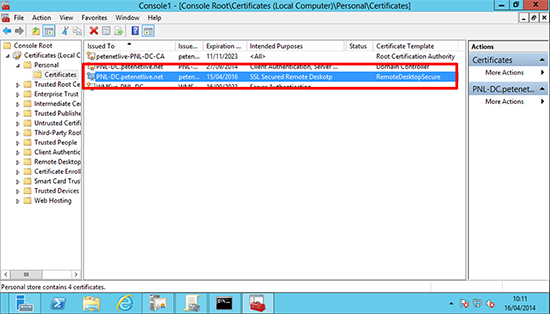
Note: This view is simply ‘Microsoft Management Console’ with the ‘Certificates (Local Computer)’ snap-in added.
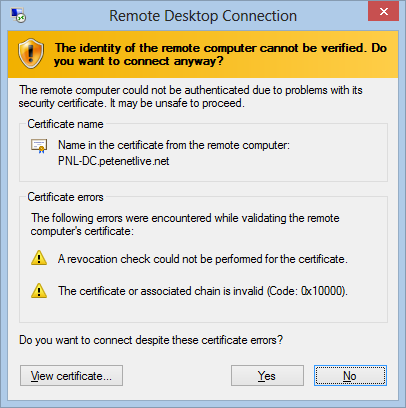
17. To prove it’s working, try connecting from a client that does not trust your Domain CA, and you should see an error something like this.
Check What Certificate RDP Is Using
You can check the thumbprint of the certificate the server is using. Windows Key+R > Regedit {Enter} > Navigate to;
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE > SYSTEM > CurrentControlSet > Control > Terminal Server > WinStations > TemplateCertificate
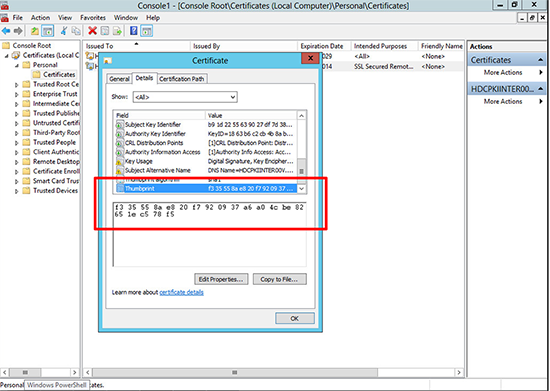
You can check this with the actual Certificate> Windows Key+R > mmc {enter} > File > Add/Remove Snap-in > Certificates > Local Computer > Open Certificates > Personal > Certificates > Locate the certificate you ‘Think’ RDP is using and you can compare its thumbprint with the registry key you found above.
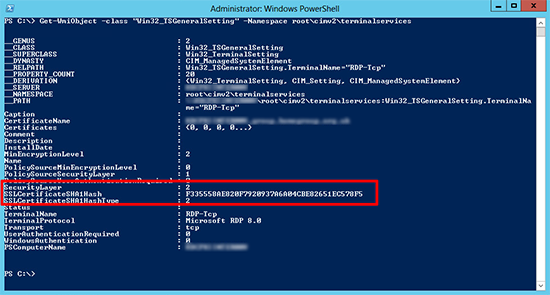
Or you can execute the following PowerShell command to get the RDP certificates thumbprint;
Get-WmiObject -Class "Win32_TSGeneralSetting" -Namespace root\cimv2\terminalservices
Related Articles, References, Credits, or External Links
NA